Data Science 101
Many of you have probably heard the term “Data Science” before, but you may or may not know exactly what it is or why it matters. Google searches will return various definitions of data science, and the job description of a data scientist will differ from one company to the next. So, what exactly is it? Data science is an interdisciplinary field which combines Statistics and Artificial Intelligence to identify patterns and extract value from complex data. It’s interdisciplinary because it involves using a combination of skills from different disciplines and we can use data science to make better decisions in every industry - finance and banking, retail, energy, insurance, healthcare, education, economics, and the list goes on. But in order to gain valuable insights from data, we need to collect it from a source, store it somewhere, transform it into formats that are easier to work with, and analyze it. These activities are all encompassed under the umbrella term “Data Science”.
In a nutshell, data scientists are highly analytical problem solvers who develop and test hypotheses to find solutions for challenges in their respective industries. They are part businessperson, part mathematician and part computer scientist. Being business savvy ensures that they have a solid understanding of the industry in which they operate, and being technically inclined helps them to develop algorithms and models to optimize processes or answer important business or research questions. For instance, a bank may be interested in building profiles that indicate what types of account holders are likely to churn. This would help them to take action before these at-risk customers decide to close their accounts. A grocery store may be interested in finding out how COVID-19 affected the sale of specific products. This can help them to understand customer buying patterns during a shock and to potentially predict future demand during a spike so that they don’t run out of inventory. An economist may be interested in finding cause and effect relationships between economic policies and employment. This information would help them to determine how strongly a policy is correlated with a desired outcome. A marketing agency may be interested in finding out which of their advertising campaigns were most successful. This would help them to improve their strategies or determine which audiences they should target for future ads. These are just a few examples of the types of questions that data science can help us to answer.
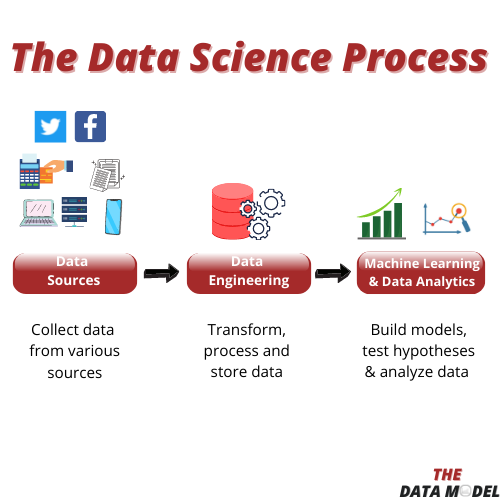
The data science process starts off with understanding the business or research question which is essentially the problem that your organization or institution wants to solve. Once you understand what the problem is and how it relates to the organization’s goals, you can collect data from relevant sources. We live in an era where data can be found in a number of places, so we can obtain it from software systems, social media, surveys, smartphones and more. Data engineering allows us to extract this data from sources of interest and transform it in order to prepare it for exploratory analysis. It is worth mentioning that data engineers do not mine data for insights, but they design, build, and maintain data management systems which are then used by data scientists and analysts. Data engineers primarily use programming languages such as Python, Java and SQL, they have strong knowledge of ETL processes, data warehousing and data lakes, and they are familiar with tools such as Apache Spark, Google Cloud Platform and Microsoft Azure. Data scientists and analysts try to understand and explain historical trends as well as predict future trends. Identifying these trends helps them to answer their organization’s questions and to recommend solutions that are supported by data. They don’t just code all day or build models all day. Data scientists and analysts always use visualization tools to create graphs, charts, tables and dashboards that help them to tell a story with the data. They use programming languages such as R, Python and SQL, and visualization tools such as Power BI and Tableau. As a result, data scientists and analysts must be great communicators as they have to translate technical findings to non-technical audiences who will eventually take their recommendations into consideration.
Ultimately, data acts as evidence that we can use to explain occurrences in business or society, and this is why data science is so important. As long as we can use facts to explain things, rather than guesses, we can make more informed decisions. This, in turn, can lead to improved profit maximization strategies, better risk management, stronger economic policies, and more impactful social programs. This post only scratches the surface of the world of data science, but we will dive deeper in subsequent blogs to see how it all works.